ARDS should first be treated to improve oxygen levels in the blood. A lack of oxygen results in organ dysfunction.
To get more
oxygen into your bloodstream, your doctor will likely use:
- Supplemental oxygen: For milder symptoms or
as a temporary measure, oxygen may be delivered through a mask that fits
tightly over your nose and mouth.
- Mechanical ventilation: Most people with
ARDS will need the help of a machine to breathe. A mechanical ventilator pushes
air into your lungs and forces some of the fluid out of the air sacs.
- The Image below displays mechanical ventilation
Image: http://studynursing.blogspot.com/2010/05/ventilator-and-its-management.html
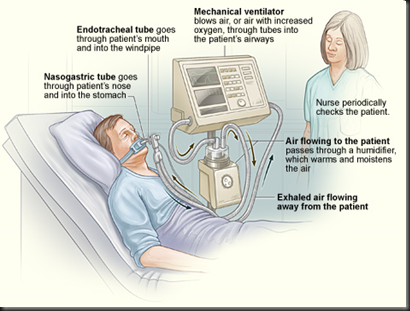
- The Image below displays mechanical ventilation
Image: http://studynursing.blogspot.com/2010/05/ventilator-and-its-management.html

Positive Pressure Ventilation to Treat ARDS
Mechanical ventilators deliver oxygen-rich air to the lungs and remove carbon dioxide from the body. The technique, also known as positive pressure ventilation, usually involves inserting an endotracheal tube into the trachea through the mouth or nose. The endotracheal tube passes through the upper airways, between the vocal cords, and into the trachea.An inflatable balloon attached to the tube at the tracheal end prevents air from escaping through the upper airways and out of the body. The end of the tube outside of the body the is connected to a ventilator (machine that forces air into the lungs by providing positive pressure).
Normally, people breathe spontaneously by contracting the large dome-shaped muscle underneath the lungs (diaphragm). When the diaphragm contracts during inhalation, the dome deflates, the volume of the chest cavity increases, and negative pressure, or a partial vacuum, is created, bringing air into the lungs. When the diaphragm relaxes during exhalation, the dome rises, the volume of the chest cavity decreases, and air is pushed out of the lungs.
Positive pressure ventilation does two things:
- It pushes air into the lungs, relieving fatigued, nonfunctioning breathing muscles.
- It creates positive pressure in the alveoli, keeping them from collapsing and pushing fluid out of the alveolar spaces.
Positive Pressure Ventilation to Treat ARDS continued...
Medication
Mechanical ventilators deliver oxygen-rich air to the lungs
and remove carbon dioxide from the body. This This usually involves inserting an
endotracheal tube into the trachea through the mouth or nose. The endotracheal
tube passes through the upper airways, between the vocal cords, and into the
trachea. An inflatable balloon attached to the tube at the tracheal end
prevents air from escaping through the upper airways and out of the body. The
end of the tube outside of the body the is connected to a ventilator (machine
that forces air into the lungs by providing positive pressure).
Positive pressure ventilation does two things:
2.
It
creates positive pressure in the alveoli, keeping them from collapsing and
pushing fluid out of the alveolar spaces.
This video demonstrates and explains Mechanical Ventilation
Medication
People with ARDS
usually are given medication to:
- Prevent and treat infections
- Relieve pain and discomfort
- Prevent clots in the legs and lungs
- Minimize gastric reflux
Medications for individuals are given to relieve pain and reduce side effects. Antibiotics or
corticosteroids can treat an infection. Blood thinners are used to
keep clots from forming in the lungs or legs.
No specific therapy exists for ARDS, yet an underlying treatment is essential. Infection is often the underlying cause of ARDS; therefore early administration of appropriate antibiotics may be necessary.
References: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/ards/, http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/ards/basics/causes/con-20030070,
No specific therapy exists for ARDS, yet an underlying treatment is essential. Infection is often the underlying cause of ARDS; therefore early administration of appropriate antibiotics may be necessary.
References: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/ards/, http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/ards/basics/causes/con-20030070,
http://www.healthcommunities.com/ards/treatment.shtml
No comments:
Post a Comment